Css width vw
Author: m | 2025-04-24

What is the vw unit in CSS? The vw unit in CSS measure the viewport width. The viewport is the area of the browser in which a website is displayed. The vw unit allows you to easily measure the width of the viewport

CSS viewport width (vw) - Uxcel
{ height: 100vh; /* Takes the full height of the viewport */}This approach works well on desktop but can cause jarring behavior on mobile as the viewport height changes dynamically.The Fix:A common solution to this problem is using CSS custom properties and JavaScript to calculate and update the correct height dynamically. This ensures the height remains stable even when the viewport changes on mobile devices.// Calculate the real viewport height and set it as a custom propertyfunction updateVH() { let vh = window.innerHeight * 0.01; document.documentElement.style.setProperty('--vh', `${vh}px`);}window.addEventListener('resize', updateVH);updateVH(); // Call on initial loadThen, in your CSS, you can use this custom property:.hero { height: calc(var(--vh, 1vh) * 100); /* Uses the calculated viewport height */}This method ensures that your design remains consistent, even on mobile browsers with dynamic UI elements.Pitfall #2: Scrollbars and Viewport Width (VW)When working with VW units, another common issue is the presence of scrollbars. On some devices or browsers, vertical scrollbars take up space on the screen but are not accounted for in the viewport width. This can cause elements sized with VW to be slightly too wide, leading to unintended horizontal scrolling.The Problem:If you set an element’s width to 100vw, it will take up the entire width of the viewport, including the area occupied by a vertical scrollbar. This can push content slightly beyond the viewport, causing a horizontal scrollbar to appear.Example:.container { width: 100vw; /* Includes scrollbar width, causing overflow */}On browsers where scrollbars overlap the content (such as macOS browsers with hidden scrollbars), this may not be a problem. But on Windows or other platforms where scrollbars take up space, the container will be wider than the visible area, leading to horizontal scrolling.The Fix:To avoid this issue, use a combination of CSS and JavaScript to calculate the correct width, excluding the scrollbar. You can use 100% width instead of 100vw, or dynamically adjust the width to account for the scrollbar:.container { width: 100%; max-width: 100vw; /* Ensures no overflow even with scrollbars */}Alternatively, use JavaScript to calculate the difference between the viewport width and the scrollbar:function updateContainerWidth() { let vw = window.innerWidth - document.documentElement.clientWidth; document.documentElement.style.setProperty('--container-width', `${vw}px`);}window.addEventListener('resize', updateContainerWidth);updateContainerWidth();This approach gives you more precise control over the element’s width and prevents the appearance of unexpected scrollbars.Pitfall #3: Issues with Nested Flexbox and Viewport UnitsViewport units can also cause issues when combined with Flexbox layouts, particularly when flex containers are nested. In some cases, using VW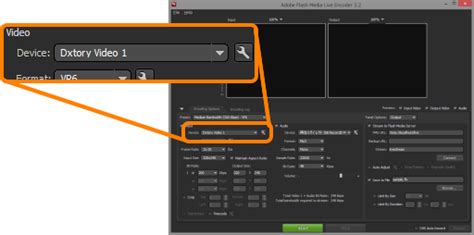
Ignoring scrollbar width in CSS vw? - Hashnode
日本住宿物語 大家都在找解答 css vmax 2023年8月8日—...方面,「vh」和「vw」分別代表視窗的高度和寬度百分比,特別適合實現響應式設計。「vmin」和「vmax」則根據視窗的最小或最大CSS,CSS應用,css,CSS教學. 2023年8月8日 — ... 方面,「vh」和「vw」分別代表視窗的高度和寬度百分比,特別適合實現響應式設計。「vmin」和「vmax」則根據視窗的最小或最大CSS, CSS應用, css, CSS教學. 取得本站獨家住宿推薦 15%OFF 訂房優惠 本站住宿推薦 20%OFF 訂房優惠,親子優惠,住宿折扣,限時回饋,平日促銷 CSS中如何使用视窗单位_CSS3, vw, vh, vmin | css vmax 这些单位是 vw , vh , vmin 和 vmax 。它们都代表了浏览器(视窗(Viewport))尺寸的比例和窗口大小调整产生的规模改变。 比方说我们有一个 1000px ... Read More 搞清楚CSS單位px、em、rem、vh、vw | css vmax 搞清楚CSS單位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax. 編程 · 發表 2016-11-04. [摘要:1、px:相對少度單元。像素px是相對表現器屏幕區分率而行的。 2、em:相對少度 ... Read More MinMaxing | css vmax 在以前浏览过的文章当中(点这查看),我发现了很有用的CSS单位: vw 和 vh 。但与其相关的单位 vmin 和 vmax 却远不为人知,且知之甚少。 Read More 谈谈一些有趣的CSS题目(25) | css vmax 谈谈一些有趣的CSS题目(25)-- vh、vw、vmin、vmax 知多少 #15. Open. chokcoco opened this issue on May 3, 2017 · 4 comments. Open ... Read More 前端技術 | css vmax vh、vw、vmin、vmax 是css3的新單位,是指裝置的畫面高度及寬度百分比。 1vw=1% 螢幕的寬度. 1vh=1% 螢幕的高度. 1vmin ... Read More [筆記] 好用的css 3新單位vh vw 讓你的圖片可以隨著螢幕大小而 ... | css vmax vmin和vmax. 另外,還有一個補充的單位是vmin,這個的意思是幫我抓取「長或寬 ... Read More CSS Units | css vmax Many CSS properties take "length" values, such as width , margin , padding , font-size , etc. Length ... vmax, Relative to 1% of viewport's* larger dimension, Try it. Read More Guide to CSS Viewport Units: vw, vh, vmin | css vmax Viewport-percentage lengths, or viewport units as they are more frequently referred to, are responsive CSS units that allow you to define ... Read More 搞清楚CSS单位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax | css vmax 搞清楚CSS单位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax. 原创 逍遥不羁 最后发布于2016-04-11 11:53:04 阅读数15872 收藏. 发布于2016-04-11 11:53:04. 分类专栏: css. Read More CSS單位大全(px,em,rem,vh,vw,vmin | css vmax 2021年5月11日 — CSS單位大全(px,em,rem,vh,vw,vmin,vmax) · px. px是相對顯示器的解析度及螢幕寬度決定,不是一個絕對單位。 · em. em是相對單位。 · rem. rem也是相對單位, ... Read More 搞清楚CSS單位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax | css vmax 搞清楚CSS單位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax. 分類:編程 時間:2016-11-04. [摘要:1、px:相對少度單元。像素px是相對表現器屏幕區分率而行的。 Read More Day 4 - 什麼是vh,vw? | css vmax 這裡我們會討論4 個單位元素, vh , vw , vmin ,和 vmax 。 定義. vh. 螢幕可視範圍高度的百分比. vw. 螢幕可視範圍寬度百分比. vmin. vh 和 vw 中比較小的值. vmax. Read More MinMaxing | css vmax 2016年11月1日 — MinMaxing: Understanding vMin and vMax in CSS · vmin uses the ratio of the smallest side. That is, if the height of the browser window is less ... Read More vh, vw, vmin | css vmax CSS 5 個常用的單位 | css vmax MinMaxing理解CSS中的vMin和vMax | css vmax 2021年4月6日 — 在以前浏览过的文章当中(点这查看),我发现了很有用的CSS单位:vw和vh。但与其相关的单位vmin和vmax却远不为人知,且知之甚少。这是非常不幸的, ... Read More 新單位vw、vh、vmin、vmax使用詳解(附樣例) | css vmax 2020年5月29日 — CSS3 又引入了新單位:vw、vh、vmin、vmax。 ... 這裡就可以用到vmin 和vmax。 ... 一些設置CSS 長度的屬性有width, margin, padding, font-size, ... Read More CSS Viewport 宽度单位vh、vw、vmin、vmax、 使用指南 | css vmax 2022年2月15日 — CSS Viewport 宽度单位vh、vw、vmin、vmax、 使用指南. CSS Viewport 单位是真正的响应式长度单位,它们会随着浏览器调整大小而改变其值,这使得它们 ... Read More MinMaxing理解CSS中的vMin和vMax | css vmax 2021年4月6日 — vmax:使用视窗宽与高中的最大的那个。 它们能被用在什么地方? vim 和 vmax 是CSS方向媒体查询( @media screen and (orientation : portrait) 或 ... Read More 【CSS】CSS 單位指南與應用大全(em, rem, vh, vw, % | css vmax 2023年8月8日 — ... 方面,「vh」和「vw」分別代表視窗的高度和寬度百分比,特別適合實現響應式設計。「vmin」和「vmax」則根據視窗的最小或最大CSS, CSS應用, css, CSS教學. Read More 認識CSS3的新單位vh、vw | css vmax 另外,還有一個要補充的單位是vmin,意思是選取「長或寬較小的百分比」,反之vmax意思就是選取「長或寬較大的百分比」。 透過這些單位,就可以更容易設計可隨視窗大小變動 ... Read More CSS Viewport 宽度单位vh、vw、vmin、vmax、 使用指南 | css vmax 2022年2月15日 — CSS Viewport 单位是真正的响应式长度单位,它们会随着浏览器调整大小而改变其值,这使得它们在现代Web 应用程序中更加灵活。 Read More CSS3 | css vmax 2022年5月2日 — (1) vw、vh、vmin、vmax 是一种视窗单位,也是相对单位。它相对的不是父节点或者页面的根节点。而是由视窗(Viewport)大小来决定的,单位1,代表类似于 ... Read More css中vhvwvmaxvminremem介绍 | css vmax vw是根据视图(viewport)的宽度来定,假设宽度为width,那么1vw=1/100*width。假设浏览器宽度为200,那么1vw=2px。 vmin/vmax. 就是vh,vw中的较大者,较小 ... Read More Units in CSS (em, rem, pt, px, vw, vh, vmin, vmax, ex | css vmax 2019年7月29日 — vmax is the maximum between the viewport's height or width in percentage depending on which is bigger. If you like my content, you might want to ... Read More 【CSS】CSS 單位指南與應用大全(em, rem, vh,css - sizing a width by VW units while assuring a minimum width
Viewport در طراحی وب به بخش قابل مشاهده یک صفحه در مرورگر یا دستگاه کاربر گفته میشود و بسته به اندازه صفحه نمایش، متغیر است. واحدهای Viewport مانند vw، vh، vmin و vmax در CSS، امکان استفاده از اندازههای وابسته به Viewport را فراهم میکنند. این واحدها به خصوص در طراحیهای واکنشگرا بسیار مفید هستند. در این مقاله، به معرفی Viewport و واحدهای مرتبط با آن میپردازیم و کاربردهای آنها در CSS را بررسی میکنیم.آشنایی با ViewportViewport به ناحیهای از صفحه اشاره دارد که کاربران میتوانند بدون نیاز به اسکرول، مشاهده کنند. اندازه Viewport در دستگاههای مختلف (مانند دسکتاپ، تبلت و موبایل) متفاوت است و CSS قابلیتهای مختلفی را برای تنظیم عناصر متناسب با اندازه Viewport فراهم میکند.به عنوان مثال: در دسکتاپ، Viewport معمولاً بزرگتر است. در موبایل، Viewport کوچکتر است و ممکن است کاربر نیاز به اسکرول داشته باشد. معرفی واحدهای Viewportواحدهای Viewport به شما امکان میدهند که اندازه عناصر را بر اساس اندازه Viewport تعیین کنید. این واحدها بسیار واکنشپذیر هستند و به خصوص در طراحیهای پاسخگو مفید واقع میشوند.واحدهای رایج Viewport vw (Viewport Width): یک واحد vw برابر با 1٪ از عرض Viewport است. vh (Viewport Height): یک واحد vh برابر با 1٪ از ارتفاع Viewport است. vmin: کوچکتر از عرض و ارتفاع Viewport را میگیرد و 1٪ آن را نشان میدهد. vmax: بزرگتر از عرض و ارتفاع Viewport را میگیرد و 1٪ آن را نشان میدهد. مثالهایی از استفاده از واحدهای Viewportاستفاده از vw و vh برای تنظیم عرض و ارتفاع.full-width-box { width: 100vw; height: 50vh; background-color: lightblue;}در اینجا: width: 100vw عرض عنصر را برابر با 100٪ عرض Viewport تعیین میکند. height: 50vh ارتفاع عنصر را برابر با 50٪ ارتفاع Viewport تنظیم میکند. استفاده از vmin برای اندازهدهی متناسب.square-box { width: 50vmin; height: 50vmin; background-color: lightcoral;}در اینجا: 50vmin به عنوان اندازه هر ضلع مربع انتخاب شده که در دستگاههای مختلف نسبت ثابتی خواهد داشت. استفاده از vmax برای حداکثر اندازهدهی.banner { font-size: 5vmax;}در اینجا: font-size: 5vmax اندازه فونت را بر اساس بزرگترین بعد Viewport تنظیم میکند، که برای حفظ وضوح متون در دستگاههای مختلف مناسب است. کاربردهای رایج Viewport Units در طراحی وبساخت بخشهای تمام صفحهواحدهای Viewport میتوانند برای ایجاد بخشهایی با اندازه تمام صفحه استفاده شوند..full-screen-section { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; background: url('background.jpg') no-repeat center center; background-size: cover;}در اینجا: بخش full-screen-section کل صفحه را پوشش میدهد و برای طراحیهای تک صفحهای و اسلایدها بسیار مناسب است. تنظیم فونت واکنشگرابا استفاده از واحدهای Viewport، میتوانید فونتهایی بسازید که نسبت به اندازه صفحه واکنشگرا باشند..responsive-heading { font-size: 3vw;}در اینجا: font-size: 3vw باعث میشود که اندازه فونت متناسب با عرض Viewport تنظیم شود و در دستگاههای مختلف به صورت پویا تغییر کند. ساخت بخشهای منطبق با نسبت ابعادواحدهای Viewport به شما این امکان را میدهند که بخشهایی با نسبت ابعاد ثابت در دستگاههای مختلف ایجاد کنید..aspect-ratio-box { width: 100vw; height: 56.25vw; /* برای نسبت 16:9 */}در اینجا: height: 56.25vw ارتفاع با نسبت 16:9 تنظیم شده تا در نمایشگرهای مختلف نسبت تصویر ثابت بماند. ترکیب واحدهای Viewport با واحدهای دیگر در CSSگاهی اوقات برای طراحیهای پیچیدهتر، میتوانید واحدهای Viewport. What is the vw unit in CSS? The vw unit in CSS measure the viewport width. The viewport is the area of the browser in which a website is displayed. The vw unit allows you to easily measure the width of the viewport osbo.com CSS Units vw. vw. Description; Syntax; Examples; Links; Description. The vw unit for CSS specifies 1% of the default viewport’s width. Syntax number vw.css - Is it possible to calculate the Viewport Width (vw) without
Comprendiéndo el concepto de CSS VWEl término CSS VW se refiere a un tipo de unidad de medida en el lenguaje de hojas de estilo en cascada (CSS). VW significa Viewport Width (Ancho de la ventana de visualización) y permite a los desarrolladores definir medidas de elementos en relación con el ancho total de la ventana del navegador, facilitando la creación de diseños responsivos. En términos sencillos, 1vw equivale al 1% del ancho total de la ventana.Cómo funciona CSS VWLa unidad de medida VW es especialmente útil cuando se requiere que un elemento se redimensione dinámicamente basándose en el ancho de la pantalla. Por ejemplo, si un elemento tiene un ancho configurado como 50vw, sin importar el tamaño de la ventana del navegador, ese elemento siempre ocupará el 50% del ancho de la ventana. Esto se traduce en una mayor flexibilidad y control sobre el comportamiento del sitio web en diferentes tamaños de pantalla, desde dispositivos móviles hasta monitores de grandes dimensiones.Uso práctico del CSS VWAdemás de poder ajustar los elementos según el ancho de la ventana del navegador, la unidad VW también puede ser utilizada para configurar el tamaño de la letra, espaciado entre elementos, alto de las secciones, entre otros. Sin embargo, es importante tener en cuenta que su uso debe combinarse con otras unidades de medida y técnicas de CSS para asegurar que el sitio web sea legible y funcione correctamente en todas las condiciones. En esencia, la unidad VW es una herramienta poderosa en el kit de herramientas de un desarrollador para crear sitios web responsivos y flexibles.Aprovecha al máximo el CSS VW en tu diseño webEl uso eficiente de las unidades de medida CSS VW puede transformar drásticamente tu diseño web, mejorando su responsividad y flexibilidad. Las unidades VW [Viewport Width] definen el ancho de la vista actual y permiten un gran control sobre cómo se ajustan los elementos a diferentes tamaños de pantalla. Esto es realmente útil cuando estás diseñando un sitio que necesita responder adecuadamente a una variedad de dispositivos, desde pantallas de escritorio hasta dispositivos móviles más pequeños.Además, el uso de las unidades VW puede facilitar considerablemente el proceso de diseño. En lugar de tener que ajustar manualmente los tamaños de los elementos en diferentes puntos de interrupción, puedes definir los tamaños en términos de VW y dejar que el navegador haga los cálculos. Esta flexibilidad puede ahorrar tiempo y esfuerzo, permitiéndotecss - Why is VW not equal to the visual width of the window?
What are CSS Units?CSS units are measurements used to specify the size of elements, fonts, and spacing in a web page. They determine how content is rendered on different devices and screen sizes. Common units include px (pixels), rem (root em), em, vw (viewport width), vh (viewport height), and percentages ( % ).What is the difference between absolute and relative units?CSS units are categorized into absolute and relative units. Absolute units (e.g., px, cm, mm) represent fixed sizes, irrespective of the context. Relative units (e.g., rem, em, %, vw, vh) depend on other factors like the root font size, parent element size, or viewport dimensions, making them more flexible for responsive designs.What are pixels (px) in CSS?Pixels are the most commonly used CSS unit. They represent a fixed size and are not affected by parent or root elements. One pixel corresponds to one dot on the screen. While they offer precision, they can hinder responsiveness.What is the difference between rem and em?rem (root em) is relative to the root element’s font size, while em is relative to the font size of the parent element. For example, if the root font size is 16px, 1rem equals 16px, and if a parent element's font size is 20px, 1em within it equals 20px.When should you use rem instead of em?rem is ideal for consistent scaling across elements, as it is always relative to the root font size. em is better for scaling elements relative to their parent, useful for nesting layouts where each element’s size adapts proportionally to its container.What are viewport units (vw and vh)?Viewport units are relative to the browser window dimensions. 1vw equals 1% of the viewport width, and 1vh equals 1% of the viewport height. They are often used for responsive typography, margins, or dynamic layouts.How does the root font size affect rem and em?The root font size defines the base size for rem. By default, browsers set it to 16px, but you can modify it using the element’s CSS property. For example, setting html { font-size: 10px; } makes 1rem equal to 10px.What does percentage (%) represent in CSS?Percentages are relative to the parent element. For example, if an element’s width is set to 50%, it will occupy half of its parent’s width. Percentages adapt to changes in the parent element's dimensions, making them ideal for responsive designs.How do CSS units impact responsive design?Responsive design benefits from relative units like rem, %, vw, and vh, which adapt to screen sizes, resolutions, and user preferences. Avoid absolute units like px for layouts intended to scale across devices.What are the best units for font sizes in CSS?rem is preferred for font sizes because it scales consistently with the root font size. em is used when you want font sizes to adapt to the parent element’s size, and px is ideal for fixed typography when responsiveness is not a priority.How are vw and vh used for layouts?Viewport units vw and vh are excellent for fluid layouts. For instance, setting width: 100vw;What is VH/VW (viewport height/ viewport width) in CSS? CSS
Combining VW and VH with other fluid units like percentages or rems can sometimes lead to conflicting behavior, where elements scale too aggressively or fail to align properly.The Problem:When combining fluid units like VW with percentages or em-based layouts, the elements may not scale proportionally, leading to awkward spacing or misaligned content.Example:.container { width: 80vw;}.text { font-size: 2rem; margin: 5%; /* Percentages and viewport units might conflict */}In this case, the text size and margin may not align well with the container, especially as the viewport resizes.The Fix:To create a more consistent fluid layout, use consistent units across your design. If you’re using viewport units for width or height, consider using them for spacing and font sizes as well to ensure a harmonious scaling experience. Alternatively, use a combination of fluid typography and CSS Grid or Flexbox to maintain a balanced layout.Example of a fluid layout with consistent units:.container { width: 80vw; padding: 5vw; /* Consistent spacing with VW */}.text { font-size: 3vw; /* Scales with viewport */}By keeping the units consistent, you avoid conflicts and ensure that all elements scale proportionally, creating a smoother, more balanced fluid layout.Conclusion: Mastering VW and VH with Best PracticesViewport units are incredibly powerful for creating responsive designs that scale effortlessly across devices. However, as we’ve seen, they can introduce a range of issues—from mobile viewport height inconsistencies to unexpected scrollbars and layout shifts. To master VW and VH, it’s important to understand their limitations and use them strategically.Here’s a summary of best practices for avoiding the pitfalls of viewport units:Use CSS custom properties and JavaScript to manage viewport height (VH) on mobile devices where the UI can change dynamically.Avoid using 100vw for full-width elements to prevent horizontal scrollbars—use 100% or adjust for the scrollbar width.Let Flexbox or Grid control layout sizes and avoid mixing viewport units with these layout techniques.Adjust for large screens using media queries to prevent elements from scaling too large.Predefine sizes for dynamic content like images or videos to prevent layout shifts during loading.By following these strategies, you can take full advantage of viewport units without falling into the common traps that can harm the user experience. At PixelFree Studio, we believe that the best designs are not only responsive but also stable and performant. By mastering VW and VH and understanding their intricacies, you can create layouts that look polished and behave predictably, no matter the device or screen. What is the vw unit in CSS? The vw unit in CSS measure the viewport width. The viewport is the area of the browser in which a website is displayed. The vw unit allows you to easily measure the width of the viewportComments
{ height: 100vh; /* Takes the full height of the viewport */}This approach works well on desktop but can cause jarring behavior on mobile as the viewport height changes dynamically.The Fix:A common solution to this problem is using CSS custom properties and JavaScript to calculate and update the correct height dynamically. This ensures the height remains stable even when the viewport changes on mobile devices.// Calculate the real viewport height and set it as a custom propertyfunction updateVH() { let vh = window.innerHeight * 0.01; document.documentElement.style.setProperty('--vh', `${vh}px`);}window.addEventListener('resize', updateVH);updateVH(); // Call on initial loadThen, in your CSS, you can use this custom property:.hero { height: calc(var(--vh, 1vh) * 100); /* Uses the calculated viewport height */}This method ensures that your design remains consistent, even on mobile browsers with dynamic UI elements.Pitfall #2: Scrollbars and Viewport Width (VW)When working with VW units, another common issue is the presence of scrollbars. On some devices or browsers, vertical scrollbars take up space on the screen but are not accounted for in the viewport width. This can cause elements sized with VW to be slightly too wide, leading to unintended horizontal scrolling.The Problem:If you set an element’s width to 100vw, it will take up the entire width of the viewport, including the area occupied by a vertical scrollbar. This can push content slightly beyond the viewport, causing a horizontal scrollbar to appear.Example:.container { width: 100vw; /* Includes scrollbar width, causing overflow */}On browsers where scrollbars overlap the content (such as macOS browsers with hidden scrollbars), this may not be a problem. But on Windows or other platforms where scrollbars take up space, the container will be wider than the visible area, leading to horizontal scrolling.The Fix:To avoid this issue, use a combination of CSS and JavaScript to calculate the correct width, excluding the scrollbar. You can use 100% width instead of 100vw, or dynamically adjust the width to account for the scrollbar:.container { width: 100%; max-width: 100vw; /* Ensures no overflow even with scrollbars */}Alternatively, use JavaScript to calculate the difference between the viewport width and the scrollbar:function updateContainerWidth() { let vw = window.innerWidth - document.documentElement.clientWidth; document.documentElement.style.setProperty('--container-width', `${vw}px`);}window.addEventListener('resize', updateContainerWidth);updateContainerWidth();This approach gives you more precise control over the element’s width and prevents the appearance of unexpected scrollbars.Pitfall #3: Issues with Nested Flexbox and Viewport UnitsViewport units can also cause issues when combined with Flexbox layouts, particularly when flex containers are nested. In some cases, using VW
2025-03-27日本住宿物語 大家都在找解答 css vmax 2023年8月8日—...方面,「vh」和「vw」分別代表視窗的高度和寬度百分比,特別適合實現響應式設計。「vmin」和「vmax」則根據視窗的最小或最大CSS,CSS應用,css,CSS教學. 2023年8月8日 — ... 方面,「vh」和「vw」分別代表視窗的高度和寬度百分比,特別適合實現響應式設計。「vmin」和「vmax」則根據視窗的最小或最大CSS, CSS應用, css, CSS教學. 取得本站獨家住宿推薦 15%OFF 訂房優惠 本站住宿推薦 20%OFF 訂房優惠,親子優惠,住宿折扣,限時回饋,平日促銷 CSS中如何使用视窗单位_CSS3, vw, vh, vmin | css vmax 这些单位是 vw , vh , vmin 和 vmax 。它们都代表了浏览器(视窗(Viewport))尺寸的比例和窗口大小调整产生的规模改变。 比方说我们有一个 1000px ... Read More 搞清楚CSS單位px、em、rem、vh、vw | css vmax 搞清楚CSS單位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax. 編程 · 發表 2016-11-04. [摘要:1、px:相對少度單元。像素px是相對表現器屏幕區分率而行的。 2、em:相對少度 ... Read More MinMaxing | css vmax 在以前浏览过的文章当中(点这查看),我发现了很有用的CSS单位: vw 和 vh 。但与其相关的单位 vmin 和 vmax 却远不为人知,且知之甚少。 Read More 谈谈一些有趣的CSS题目(25) | css vmax 谈谈一些有趣的CSS题目(25)-- vh、vw、vmin、vmax 知多少 #15. Open. chokcoco opened this issue on May 3, 2017 · 4 comments. Open ... Read More 前端技術 | css vmax vh、vw、vmin、vmax 是css3的新單位,是指裝置的畫面高度及寬度百分比。 1vw=1% 螢幕的寬度. 1vh=1% 螢幕的高度. 1vmin ... Read More [筆記] 好用的css 3新單位vh vw 讓你的圖片可以隨著螢幕大小而 ... | css vmax vmin和vmax. 另外,還有一個補充的單位是vmin,這個的意思是幫我抓取「長或寬 ... Read More CSS Units | css vmax Many CSS properties take "length" values, such as width , margin , padding , font-size , etc. Length ... vmax, Relative to 1% of viewport's* larger dimension, Try it. Read More Guide to CSS Viewport Units: vw, vh, vmin | css vmax Viewport-percentage lengths, or viewport units as they are more frequently referred to, are responsive CSS units that allow you to define ... Read More 搞清楚CSS单位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax | css vmax 搞清楚CSS单位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax. 原创 逍遥不羁 最后发布于2016-04-11 11:53:04 阅读数15872 收藏. 发布于2016-04-11 11:53:04. 分类专栏: css. Read More CSS單位大全(px,em,rem,vh,vw,vmin | css vmax 2021年5月11日 — CSS單位大全(px,em,rem,vh,vw,vmin,vmax) · px. px是相對顯示器的解析度及螢幕寬度決定,不是一個絕對單位。 · em. em是相對單位。 · rem. rem也是相對單位, ... Read More 搞清楚CSS單位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax | css vmax 搞清楚CSS單位px、em、rem、vh、vw、vmin、vmax. 分類:編程 時間:2016-11-04. [摘要:1、px:相對少度單元。像素px是相對表現器屏幕區分率而行的。 Read More Day 4 - 什麼是vh,vw? | css vmax 這裡我們會討論4 個單位元素, vh , vw , vmin ,和 vmax 。 定義. vh. 螢幕可視範圍高度的百分比. vw. 螢幕可視範圍寬度百分比. vmin. vh 和 vw 中比較小的值. vmax. Read More MinMaxing | css vmax 2016年11月1日 — MinMaxing: Understanding vMin and vMax in CSS · vmin uses the ratio of the smallest side. That is, if the height of the browser window is less ... Read More vh, vw, vmin | css vmax CSS 5 個常用的單位 | css vmax MinMaxing理解CSS中的vMin和vMax | css vmax 2021年4月6日 — 在以前浏览过的文章当中(点这查看),我发现了很有用的CSS单位:vw和vh。但与其相关的单位vmin和vmax却远不为人知,且知之甚少。这是非常不幸的, ... Read More 新單位vw、vh、vmin、vmax使用詳解(附樣例) | css vmax 2020年5月29日 — CSS3 又引入了新單位:vw、vh、vmin、vmax。 ... 這裡就可以用到vmin 和vmax。 ... 一些設置CSS 長度的屬性有width, margin, padding, font-size, ... Read More CSS Viewport 宽度单位vh、vw、vmin、vmax、 使用指南 | css vmax 2022年2月15日 — CSS Viewport 宽度单位vh、vw、vmin、vmax、 使用指南. CSS Viewport 单位是真正的响应式长度单位,它们会随着浏览器调整大小而改变其值,这使得它们 ... Read More MinMaxing理解CSS中的vMin和vMax | css vmax 2021年4月6日 — vmax:使用视窗宽与高中的最大的那个。 它们能被用在什么地方? vim 和 vmax 是CSS方向媒体查询( @media screen and (orientation : portrait) 或 ... Read More 【CSS】CSS 單位指南與應用大全(em, rem, vh, vw, % | css vmax 2023年8月8日 — ... 方面,「vh」和「vw」分別代表視窗的高度和寬度百分比,特別適合實現響應式設計。「vmin」和「vmax」則根據視窗的最小或最大CSS, CSS應用, css, CSS教學. Read More 認識CSS3的新單位vh、vw | css vmax 另外,還有一個要補充的單位是vmin,意思是選取「長或寬較小的百分比」,反之vmax意思就是選取「長或寬較大的百分比」。 透過這些單位,就可以更容易設計可隨視窗大小變動 ... Read More CSS Viewport 宽度单位vh、vw、vmin、vmax、 使用指南 | css vmax 2022年2月15日 — CSS Viewport 单位是真正的响应式长度单位,它们会随着浏览器调整大小而改变其值,这使得它们在现代Web 应用程序中更加灵活。 Read More CSS3 | css vmax 2022年5月2日 — (1) vw、vh、vmin、vmax 是一种视窗单位,也是相对单位。它相对的不是父节点或者页面的根节点。而是由视窗(Viewport)大小来决定的,单位1,代表类似于 ... Read More css中vhvwvmaxvminremem介绍 | css vmax vw是根据视图(viewport)的宽度来定,假设宽度为width,那么1vw=1/100*width。假设浏览器宽度为200,那么1vw=2px。 vmin/vmax. 就是vh,vw中的较大者,较小 ... Read More Units in CSS (em, rem, pt, px, vw, vh, vmin, vmax, ex | css vmax 2019年7月29日 — vmax is the maximum between the viewport's height or width in percentage depending on which is bigger. If you like my content, you might want to ... Read More 【CSS】CSS 單位指南與應用大全(em, rem, vh,
2025-04-09Comprendiéndo el concepto de CSS VWEl término CSS VW se refiere a un tipo de unidad de medida en el lenguaje de hojas de estilo en cascada (CSS). VW significa Viewport Width (Ancho de la ventana de visualización) y permite a los desarrolladores definir medidas de elementos en relación con el ancho total de la ventana del navegador, facilitando la creación de diseños responsivos. En términos sencillos, 1vw equivale al 1% del ancho total de la ventana.Cómo funciona CSS VWLa unidad de medida VW es especialmente útil cuando se requiere que un elemento se redimensione dinámicamente basándose en el ancho de la pantalla. Por ejemplo, si un elemento tiene un ancho configurado como 50vw, sin importar el tamaño de la ventana del navegador, ese elemento siempre ocupará el 50% del ancho de la ventana. Esto se traduce en una mayor flexibilidad y control sobre el comportamiento del sitio web en diferentes tamaños de pantalla, desde dispositivos móviles hasta monitores de grandes dimensiones.Uso práctico del CSS VWAdemás de poder ajustar los elementos según el ancho de la ventana del navegador, la unidad VW también puede ser utilizada para configurar el tamaño de la letra, espaciado entre elementos, alto de las secciones, entre otros. Sin embargo, es importante tener en cuenta que su uso debe combinarse con otras unidades de medida y técnicas de CSS para asegurar que el sitio web sea legible y funcione correctamente en todas las condiciones. En esencia, la unidad VW es una herramienta poderosa en el kit de herramientas de un desarrollador para crear sitios web responsivos y flexibles.Aprovecha al máximo el CSS VW en tu diseño webEl uso eficiente de las unidades de medida CSS VW puede transformar drásticamente tu diseño web, mejorando su responsividad y flexibilidad. Las unidades VW [Viewport Width] definen el ancho de la vista actual y permiten un gran control sobre cómo se ajustan los elementos a diferentes tamaños de pantalla. Esto es realmente útil cuando estás diseñando un sitio que necesita responder adecuadamente a una variedad de dispositivos, desde pantallas de escritorio hasta dispositivos móviles más pequeños.Además, el uso de las unidades VW puede facilitar considerablemente el proceso de diseño. En lugar de tener que ajustar manualmente los tamaños de los elementos en diferentes puntos de interrupción, puedes definir los tamaños en términos de VW y dejar que el navegador haga los cálculos. Esta flexibilidad puede ahorrar tiempo y esfuerzo, permitiéndote
2025-04-19What are CSS Units?CSS units are measurements used to specify the size of elements, fonts, and spacing in a web page. They determine how content is rendered on different devices and screen sizes. Common units include px (pixels), rem (root em), em, vw (viewport width), vh (viewport height), and percentages ( % ).What is the difference between absolute and relative units?CSS units are categorized into absolute and relative units. Absolute units (e.g., px, cm, mm) represent fixed sizes, irrespective of the context. Relative units (e.g., rem, em, %, vw, vh) depend on other factors like the root font size, parent element size, or viewport dimensions, making them more flexible for responsive designs.What are pixels (px) in CSS?Pixels are the most commonly used CSS unit. They represent a fixed size and are not affected by parent or root elements. One pixel corresponds to one dot on the screen. While they offer precision, they can hinder responsiveness.What is the difference between rem and em?rem (root em) is relative to the root element’s font size, while em is relative to the font size of the parent element. For example, if the root font size is 16px, 1rem equals 16px, and if a parent element's font size is 20px, 1em within it equals 20px.When should you use rem instead of em?rem is ideal for consistent scaling across elements, as it is always relative to the root font size. em is better for scaling elements relative to their parent, useful for nesting layouts where each element’s size adapts proportionally to its container.What are viewport units (vw and vh)?Viewport units are relative to the browser window dimensions. 1vw equals 1% of the viewport width, and 1vh equals 1% of the viewport height. They are often used for responsive typography, margins, or dynamic layouts.How does the root font size affect rem and em?The root font size defines the base size for rem. By default, browsers set it to 16px, but you can modify it using the element’s CSS property. For example, setting html { font-size: 10px; } makes 1rem equal to 10px.What does percentage (%) represent in CSS?Percentages are relative to the parent element. For example, if an element’s width is set to 50%, it will occupy half of its parent’s width. Percentages adapt to changes in the parent element's dimensions, making them ideal for responsive designs.How do CSS units impact responsive design?Responsive design benefits from relative units like rem, %, vw, and vh, which adapt to screen sizes, resolutions, and user preferences. Avoid absolute units like px for layouts intended to scale across devices.What are the best units for font sizes in CSS?rem is preferred for font sizes because it scales consistently with the root font size. em is used when you want font sizes to adapt to the parent element’s size, and px is ideal for fixed typography when responsiveness is not a priority.How are vw and vh used for layouts?Viewport units vw and vh are excellent for fluid layouts. For instance, setting width: 100vw;
2025-04-11Render (such as images, videos, or iframes), these elements can cause unexpected layout shifts, particularly if their size is defined using VW or VH.The Problem:Dynamic content can cause elements sized with VW and VH to resize or shift as the viewport adjusts. This can lead to content jumping or reflowing unexpectedly, especially when combined with lazy-loading techniques.Example:.image-container { width: 50vw; height: 50vh; /* Sized to viewport, but shifts when content loads */}If the image takes longer to load or if additional content is inserted after the page render, the element’s size might shift, leading to layout instability.The Fix:To avoid layout shifts, always provide fallback dimensions for elements that rely on dynamic content. Predefine the dimensions for images, videos, and other media to ensure that the layout remains stable as the content loads..image-container { width: 50vw; height: 50vh; background-color: #e0e0e0; /* Placeholder color to prevent shifts */}Alternatively, use the CSS property aspect-ratio to maintain a consistent size for media elements, even before they load:img { aspect-ratio: 16/9; width: 100%; height: auto;}This approach ensures that the layout remains stable and prevents unexpected shifts when dynamic content is introduced.Advanced Techniques for Handling Viewport Units in Complex LayoutsNow that we’ve covered the basic pitfalls and solutions for viewport units (VW and VH), let’s explore some advanced techniques for dealing with more complex layouts. Whether you’re working with intricate grid systems, integrating third-party widgets, or ensuring accessibility, understanding how to handle viewport units in these scenarios can make or break the success of your design.1. Combining Viewport Units with CSS Grid for Complex LayoutsCSS Grid is one of the most powerful layout tools in modern web design, and it can work harmoniously with viewport units when used correctly. Grid allows you to create intricate layouts without the need for complicated positioning or flex hacks. However, viewport units can introduce issues in grid-based layouts, especially when grid items are sized using VW or VH.The Problem:When grid items use VW or VH for their width or height, they may not respond well to changes in content size or dynamic resizing, leading to overflow issues, misalignment, or excessive white space. This can be particularly problematic in responsive designs where grid layouts need to adjust seamlessly across devices.Example:.grid-container { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr; grid-gap: 20px; height: 100vh; /* Full viewport height */}.grid-item { width: 50vw; /* May cause misalignment or overflow in the grid */}The Fix:When using CSS
2025-04-03Makes an element span the entire viewport width, while height: 50vh; makes it cover half the viewport height.What are calc() and CSS units?The calc() function combines different units for flexible layouts. For example, width: calc(100% - 20px); adjusts an element's size by subtracting 20px from its parent’s width.What are the differences between vw and %?vw is relative to the viewport, while % is relative to the parent element. Use vw for screen-wide responsiveness and % for adapting to parent elements.How do you convert px to rem?To convert px to rem, divide the px value by the root font size. For example, if the root font size is 16px, 32px equals 2rem (32 ÷ 16).What are media queries and their relation to units?Media queries use units like px or em to define breakpoints. For example, @media (max-width: 768px) targets screens smaller than 768px. Using em in breakpoints makes scaling easier.What happens when you mix units?Mixing units can lead to unpredictable behavior, especially in complex layouts. For example, combining vw and % requires careful planning to avoid unexpected overlaps or scaling issues.
2025-04-07